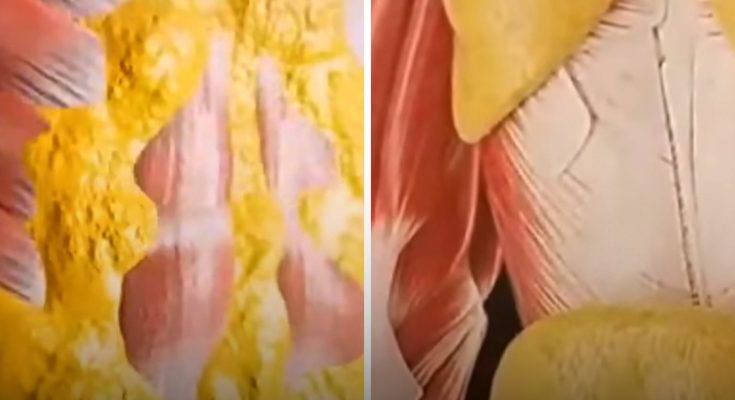
A mind-boggling simulation showing the impact fasting for a long period has on the body is currently going viral; however, some health experts aren’t quite so convinced.
People fast for a whole load of reasons, including religious observances, to promote weight loss, and even to improve cognitive function.
And while the idea of abstaining from food for a lengthy amount of time may seem abhorrent to some, others swear by the method and regularly incorporate it into their daily and weekly routines.
According to experts at Medical News Today, fasting can also help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity when completed safely.
Fasting, however, isn’t for everyone, and it’s recommended that you seek health advice before embarking on one.
However, if you’re curious, a popular YouTube page has detailed exactly what happens to your body during a 36-hour fast—and the results are wild.

Your body goes through some mind-boggling changes if you don’t eat food for 36 hours (Getty Stock Image)
What happens to your body during a 36 hour fast?
Four hours
In a 55-second video, posted to YouTube by Wellness Wise on May 6, it’s revealed that after four hours of fasting, your body stops digesting food.
According to popular practitioner Doctor Kiltz, this is what is known as the ‘catabolic phase’.
On his website, he says this period is ‘characterized by the breakdown of larger molecules of stored energy into smaller energy molecules which are mobilized to fuel your cells’.
Eight hours
So you haven’t eaten for eight hours?
Well, this is the time when sugar starts to drop in your blood and your body begins to use stored glycogen for energy instead of relying on new fuel coming in, as per the YouTube video.
12 hours
After 12 hours, your body is depleted of glucose, causing your liver to start breaking down fat into fatty acids called ketones.
This process of turning ketones into food is known as ‘metabolic switching’ and, according to the BBC, is the reason why fasting can lead to weight loss.
.jpg)
Different things happen to your body the longer you abstain from food (Getty Stock Image)
16 hours
A cellular process known as autophagy takes place after 16 hours of going without food.
As per the Cleveland Clinic, this allows a cell to disassemble its junk parts and repurpose the salvageable bits and pieces into new, usable cell parts.
Dr Hiltz explains that exercise and resistance training also helps the autophagy process because if it gets disrupted, it can cause ‘problems associated with abnormal cell growth’. Yikes.
24 hours
A full day without food is a pretty long time for most, but this 24-hour mark is where major cellular repair takes place in the human body.
According to the YouTube video, which has been viewed more than eight million times, your body is fully in fat-burning mode, reducing inflammation and improving insulin sensitivity.
30 hours
The growth hormone spikes 30 hours after fasting, which reportedly helps to preserve muscle and promote fat loss.
The YouTube video also states that this is the period where ‘deep healing’ begins.
36 hours
If you fast for 36 hours then you’ve reached the stage of maximum autophagy where your body regenerates tissues and boosts your metabolism.
This full-body reset can be extended to upwards of 72 hours if you want, too.
What do researchers say about fasting?
Experts are divided on whether or not fasting is good for the body, with some claiming a lack of human-backed studies renders making conclusions difficult.
“There [are] a lot of proposed benefits to [running on fats]. But a lot of the research hasn’t really [been borne out in] human beings. So we don’t see dramatic health benefits, certainly in the short term,” James Betts, professor of metabolic physiology at the University of Bath, told The Guardian.
Meanwhile, studies have also found that people who regularly fast more than 16 or 18 hours a day have a higher risk of gallstones, as per News In Health.
Other potential fasting side effects include intense hunger and food cravings, various digestive issues, irritability and low moods. Mark Mattson, a Johns Hopkins neuroscientist, argues that there are a myriad of benefits that come with fasting.
“Many things happen during intermittent fasting that can protect organs against chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes, heart disease, age-related neurodegenerative disorders, even inflammatory bowel disease and many cancers,” he says.
Remember, everyone reacts differently to fasting—so it’s worth checking with your medical professional before taking part in the practice.
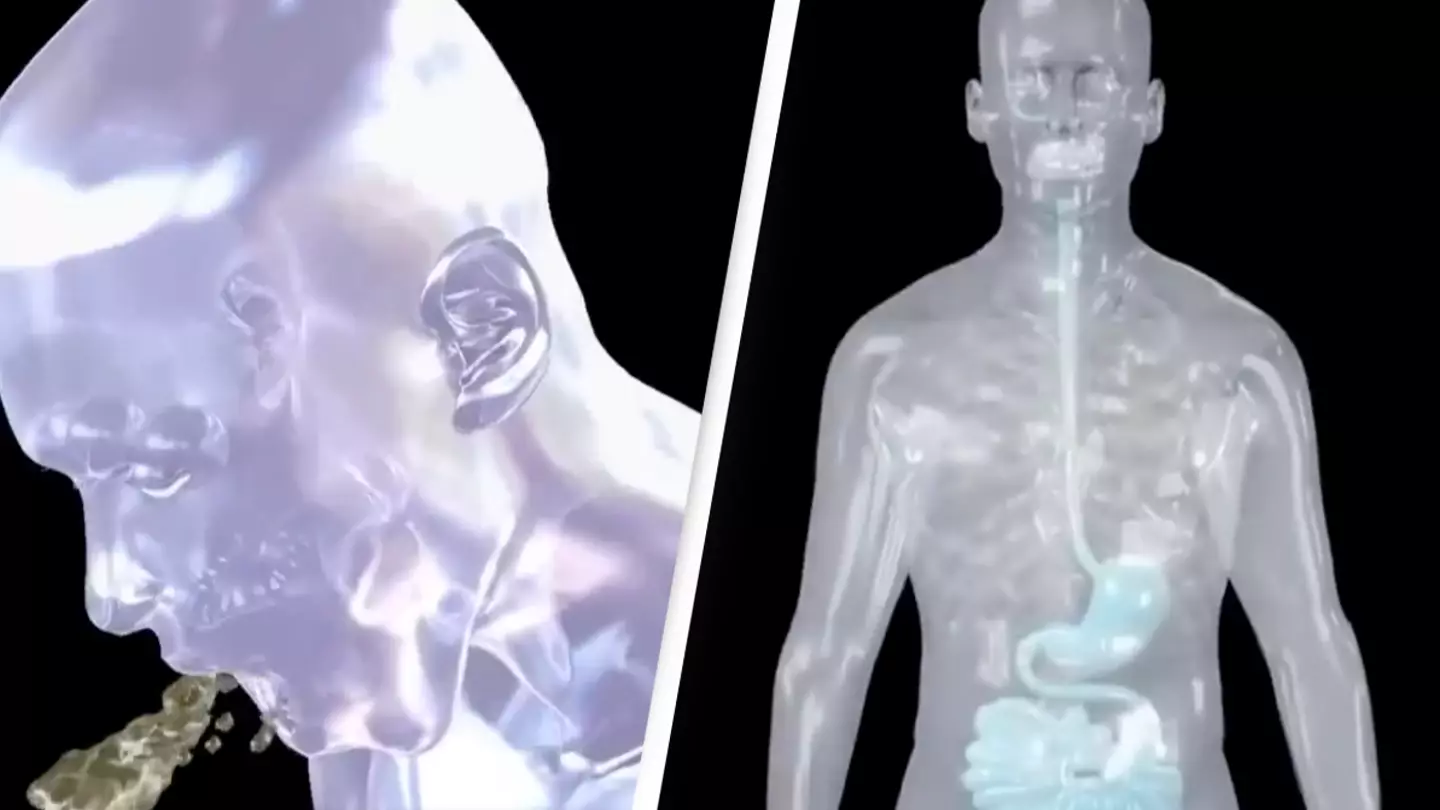
A simulation revealing what happens internally when you throw up is causing social media users to ‘almost vomit’ just from watching it.
We all know what it looks like when we vomit – sitting there, our head in our hands as we stare into the abyss of the toilet bowl, questioning why we said yes to that extra shot the night before or didn’t pay as close attention to the sell by date on that packet of prawns.
When you’re retching that last remaining bit of acid up, you may see the contents of the night before staring back at your blood shot eyes and be able to identify what’s come out of you, but do you know what’s actually going on inside in your body when you’re puking last night’s dinner up?
What happens when you vomit?
A simulation – credited to its respective owner and shared to Instagram by account @today_knowledges – reveals what happens internally before the sick spews out of your mouth and into the toilet – or on the side of the road, a bowl or hopefully just anywhere that’s not a taxi.
The video depicts the small intestine, pyloric sphincter, stomach wall and oesophagus, showing a green liquid sitting low down in the stomach. Along comes another little globule of neon green through the small intestine moving up to join the larger blob, followed by another until the stomach is full.
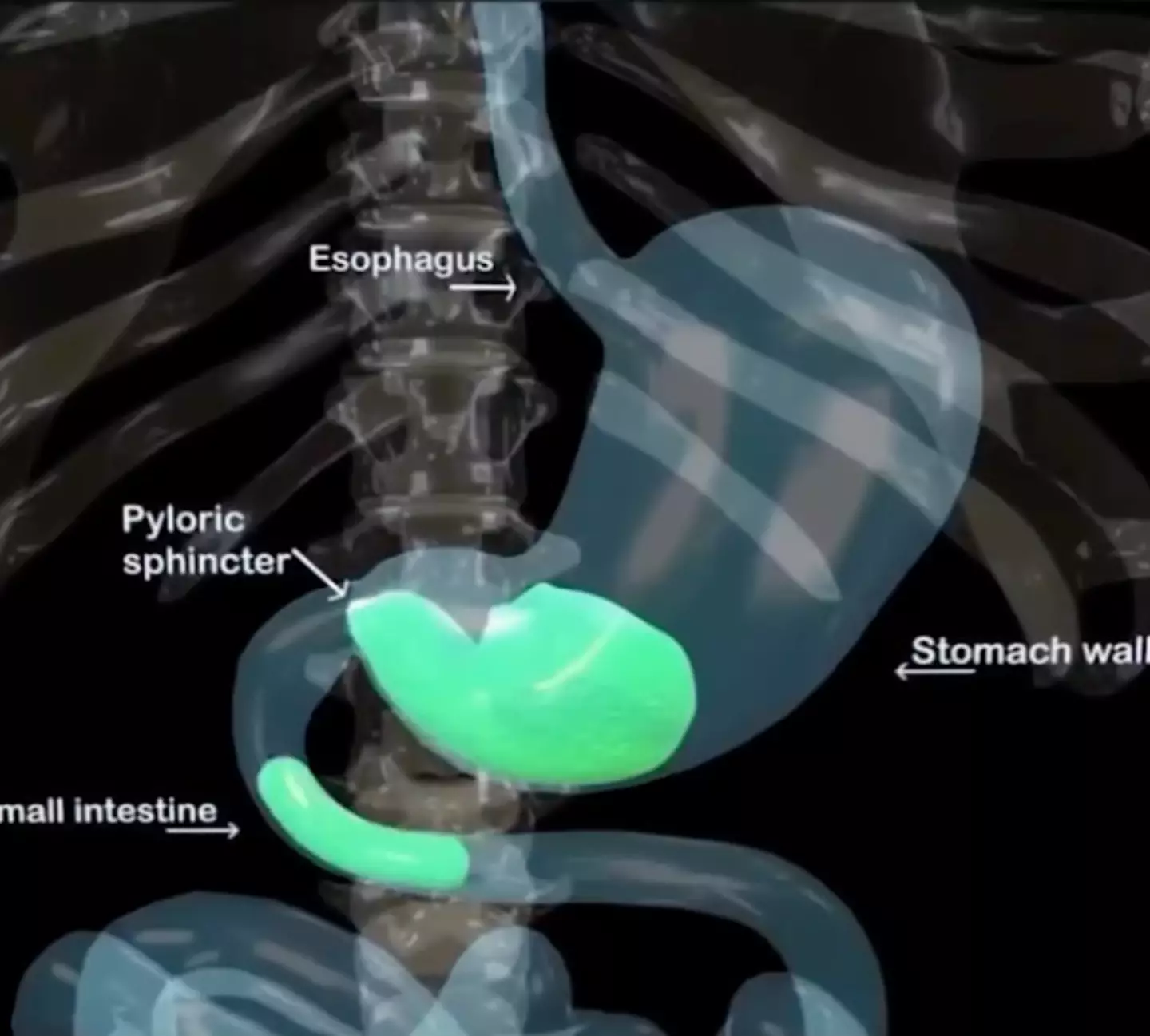
The simulation shows what happens in your body (Instagram/today_knowledges)
And that’s when the retching will begin to kick in, the diaphragm and abdomen shown contracting, the vagus and splanchnic nerves sending signals down to the oesophagus and then up the vomit travels and out it comes.
The science behind vomiting
Science Focus explains that when your body senses a ‘threat’ – i.e. toxic chemicals such as too much alcohol or ‘stress hormones in the blood, swaying motions or an upset stomach’ – these chemicals and hormones are ‘detected by the brain’s chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ)’.
The inner ear is reportedly more sensitive at picking up swaying motions and the vagus nerve an upset stomach and once the CTZ picks up either of these signals, a chain reaction gets underway.
First off your mouth will produce extra saliva ‘to protect your mouth and teeth from incoming stomach acid’.
Next, your diaphragm will begin to ‘contract in a few short pulses’ essentially in a bid to pressurize the stomach and push the sick up and out.
The glottis – located around your throat area – ‘closes’ to ‘seal the airway’ so nothing gets in or out of the lungs.
Your abdominal muscles double down on the contracting motion your diaphragm has started off, increasing pressure further to really encourage the toxicity in your body up and out.
Oh and if that wasn’t all delightful enough already, your ‘sympathetic nervous system raises your heart rate’ so you’ll end up nice and sweaty too.
Joyful – as one Twitter user said: “I think I could’ve went without knowing how this happens , I can’t stand the feeling.”
“I almost vomited seeing this,” another added.
Sober November anyone?

We’ve all heard of the five-second rule, right?
The age-old rule has certainly stood the test of time, with many of us picking up food off the floor and continuing to eat if it’s been less than five seconds.
I mean, not every floor is the same. Some are going to be a lot dirtier than others.
As a result, people have started to question if the rule should apply to every surface – particularly public ones.
We’ve learned from scientists over the years that a few germs here and there are good for the immune system.
However, after seeing a video on X earlier this year, many social media users have been calling for the five-second rule to be scrapped altogether.

Who’d thought flies could be such pests? (Getty Stock Image)
The revelation involves the work of, arguably, our most annoying insect – the fly.
Nothing ruins a stupendous summer picnic more than the buzzing of flies swarming your food.
And we’re quick to simply waft them away, even if they may have landed on our sausage rolls for a few seconds.
But should we really be throwing them away after such an incident occurs?

Many think the five-second rule should be scrapped. (Getty Stock Image)
It might not be a shock that flies don’t eat like humans – they don’t have teeth and consequently, cannot chew.
Instead, they opt for vomiting a concoction of enzymes that break down the food on your plate, making it easier for them to slurp up and digest.
Lovely, eh?
The viral video showing how exactly they do this, was created by YouTuber, Zack D. Films.
And while the knowledge isn’t breakthrough, people on social media have really decided to rethink what they’ll do with their munch next time a fly lands on it or they drop their food in a public place.
By following the five-second rule, it will probably collect less bacteria than food sitting there for a longer time. However, bacteria can actually attach to your food as soon as it hits the ground so it might be safer just to chuck it away.
One person on X said: “This is even more gross than I had imagined.”
Another said: “Ew, new revulsion unlocked.”
But it isn’t just their vomit that is problematic, their feet are also an issue.
One user pointed out: “Flies are on poop all day.
“And they are throwing it up on your food and particles from the feet are also faecal matter.”
But some people didn’t seem too bothered about the new discovery, one person actually thanked the flies, saying: “If it is putting digestive enzymes in my food I guess that will help me digest it as well.”
That’s definitely one way of looking at it…
Someone else offered a more sensible solution all round and said: “Just remove the chunk the fly was busy on then continue enjoying your food.”

A dentist has shared insight into the impacts that GLP-1 medications such as Ozempic can have on teeth after searches into the subject soared.
GLP-1 plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar, appetite, and digestion, and while it is naturally occurring hormone in the body, medications using the hormone can also be used to help treat type 2 diabetes.
It’s this condition that the drugs are typically prescribed for, but their impact on appetite and digestion mean they are also popular with people trying to lose weight – despite the fact Ozempic hasn’t been approved by the FDA for weight loss.
As members of the public continue to research the drugs and how they may affect them, a simulation revealed how Ozempic works on the body to ‘activate the part of the brain that make you feel full, reducing your appetite’.
Among the questions people have about Ozempic include whether it can have an impact on your teeth, with Google trend data cited by Hello! revealing that searches for ‘Ozempic + Teeth’ surged by 216 percent in just the one week.
To address this concern, dentist Dr. Sofina Ahmed of Viva Dental spoke to the publisher about how GLP-1 medications might impact your mouth and teeth.
Dr. Ahmed pointed to symptoms such as dry mouth and increased sensitivity in the mouth as results of these kinds of drugs, saying: “It can be a surprise for patients. They focus on weight loss and don’t realize how much it can affect oral health. But saliva, chewing activity, and hormonal balance all play a vital role in maintaining a healthy smile.”
Dry mouth and infections
The use of GLP-1 medications can cause a reduction in the amount of saliva your body produces, which in turn can leave teeth vulnerable to disease and decay.
The dentist explained: “Without enough saliva, food particles and acids aren’t washed away. This creates the perfect environment for bacteria to thrive.”
A dry mouth can also make fungal infections and ulcers on the tongue, gums and cheeks more likely.

GLP-1 medications can cause dry mouth and sensitivity (Getty Stock Photo)
Increased sensitivity and sunken smiles
Patients taking GLP-1 medications have reported increased pain when eating foods that are particularly hot, cold or sweet – and if left untreated, Dr. Ahmed warned that the impacts can ‘lead to enamel erosion or receding gums’.
In turn, receding gums can then impact the look of your face overall.
The dentist explained: “Fat loss in the cheeks and jawline can cause gums to shrink and smiles to look aged or sunken.”
Increased risk of cavities
A knock-on effect from the use of GLP-1 medications is a change of diet, including a reliance on caffeine and low carbs. However, this intake can be harmful to teeth, as the dentist said: “Caffeine, protein fermentation and fewer fibrous foods create a more acidic environment. Acid weakens enamel and raises the risk of cavities and ulcers.”
Similarly, a reduction in chewing – due to a reduction in eating – can be harmful for teeth, as Dr. Ahmed said: “Chewing stimulates saliva production and helps cleanse teeth naturally. Less chewing equals faster plaque build-up.”

Chewing helps cleanse teeth (Getty Stock Photo)
How to tackle impacts
Offering advice to patients who may be using GLP-1 medications, Dr. Ahmed encouraged people to drink water ‘consistently throughout the day’, potentially adding a sugar-free electrolyte tablet to help with absorption.
“A humidifier at night can also prevent overnight dryness,” she said.
Sucking on mints or chewing sugar-free gum can help boost saliva production, and the use of a fluoride-rich toothpaste can also be beneficial, with the dentist recommending that patients ask professionals about a prescription toothpaste if any sensitivity or decay worsens.
Other ways to stay healthy include avoiding highly acidic and sugary snacks, considering getting a night guard to avoid grinding your teeth, and taking probiotic lozenges or oral probiotics to help restore healthy oral bacteria.
Most important, Dr. Ahmed warned people to tell your dentist if you’re taking GLP-1 medications, as it can influence treatment decisions and monitoring plans.

A doctor has issued a warning about why you should only drink soda ‘reasonably and sparingly’ after a man ended up collapsing from excessive consumption, causing devastating health effects.
YouTube channel Chubbyemu – which documents medical cases to raise awareness – has revealed what happened when a patient – nicknamed BA – drank seven liters of soda every day for ‘at least’ a decade.
The patient, a 48-year-old dad, was admitted to the emergency room ‘with sudden onset weakness’.
The doctor explained BA ‘was a dad living a normal life’ but at the age of 30, he got a new job and his office stocked ‘free, unlimited soda for employees to drink’.
Prepare to start looking at those free sodas your office offers a bit differently…
The video explains that BA slowly began to drink more and more soda until it became an addiction – and it had scary impacts on his body.

Put the sugary caffeinated drink down… (Getty Stock Images)
‘The more he drank the thirstier he got’
It’s reported BA would ‘wake up thirsty’ and immediately reach for ‘his normal morning soda’.
“But the more he drank, the thirstier he got. In the bathroom, for the 10th time in two hours.”
The dad became ‘short of breath’ and suffered from stomach pain alongside experiencing ‘brain fog’ which later caused him to ‘stutter and slur his words’.
And ultimately, BA ended up in the hospital, having been found unconscious at his desk.

The patient drunk seven liters of soda every day for a decade (annabogush/Getty stock image)
Devastating health consequences of seven liters of soda everyday for 10 years
BA had gone into a ‘diabetic coma’ – the sugary nature of the soda having spiked his blood sugar levels ‘sky high for at least the last three months’.
It’s reported BA also experienced high blood pressure and high cholesterol too.
However, with BA having not recognized his soda habit as being a potential cause, he didn’t mention it to doctors and so was simply told to adopt a healthier diet and start working out.
He did adapt to zero sugar sodas half the time, but after leaving his job, he went and bought multipacks for himself.
And one day, struggling to stand after getting out of bed one morning and urinating frequently again, he ended up collapsing.
This time, the medical team noticed BA’s ‘profound muscle weakness’ as well as his history of diabetes, high blood pressure and cholesterol – but they also pinpointed a diagnosis of ‘hypokalemia’.
The patient kept drinking sodas in hospital (Witthaya Prasongsin/Getty stock image)
‘Life-threatening’ consequences
Hypokalemia is a low presence of potassium in the blood and BA’s was ‘life-threateningly low’.
And it was later discovered this meant BA’s kidneys were ‘shutting down’ too, alongside his muscles being ‘damaged’ and ‘spilling their contents out’ – something known as ‘rhabdomyolysis’.
Doctors placed BA on IV fluids but he suffered from a dry mouth and ‘massive headache,’ ringing up his wife to bring him something to quench his thirst – soda.
His headache and dry mouth went away, but the next day his results showed he still had hypokalemia and had made 15.1 liters of urine despite only having 3.78 liters through the IV.
Water was passing straight through him and his kidneys wasting the potassium doctors were trying to give him. But how could doctors help BA?
A student reportedly spotted BA being delivered sodas from his wife and did some digging, finding out the sweetening and caffeine in the soda ‘explained everything happening to BA’.

He was even getting sodas snuck into hospital (Rapeepong Puttakumwong/Getty stock image)
Why excess sugar and caffeine consumption can be so dangerous
“In the kidneys, huge excess sugar from drinking one to two gallons of soda every day for 10 years can make it harder to absorb water because the water will want to stay with the sugar,” the doctor explains.
The other problem is caffeine – ‘blocking inhibition’ and stopping a molecule in the body from helping to dilate blood vessels to allow more blood to flow through the brain and heart and promote sleep.
The molecule also helps the kidneys hold onto water by reabsorbing sodium, so the caffeine in the sodas caused the sodium to stay in the urine, which led BA to lose so much fluid.
Excess urine led to BA’s muscle proteins floating around in his blood, leading to his kidneys shutting down and muscles weakening.
What happened to BA?
Thankfully, medics were able to help him in the end.
BA was told to lay off the sodas and after he did, his blood potassium levels started to normalise, kidney function returned to normal and muscle weakness went away – ‘some baseline function achieved again’.
The doctor warns diet soda still has caffeine in it too. And diet caffeine free sodas? Well, they can still pose various risks.
The doctor adds: “So take the study results with what you will. Type 2 diabetes and all its comorbidities like heart problems and nerve damage. Hypokalemia and all its consequences and kidney stones are what we’re thinking of when we’re speaking of excess chronic soda ingestion.”
So, ‘consume reasonably and sparingly’ but ‘if you don’t need to put it in your body, don’t put it in your body’.



